Order of Operations
The order of operations dictates the sequence in which mathematical operations should be performed to ensure consistent results.
It stands for:
- Parentheses
- Exponents (including roots, such as square roots)
- Multiplication
- Division
- Subtraction
The order of operations dictates the sequence in which mathematical operations should be performed to ensure consistent results.
Here’s a detailed explanation of each step:
1. Parentheses (P)
Operations inside parentheses (or brackets) should be performed first. This includes nested parentheses, which are handled from the innermost to the outermost.
Example:
(3+2) × 5
First, solve the expression inside the parentheses:
5×5=25
Next, calculate all exponents (powers and roots).
Example:
23+ 4
8+4=12
These operations are handled from left to right, whichever comes first. Multiplication does not always come before division.
Example:
20 ÷ 4 × 2
5×2=10
4. Addition and Subtraction (AS)
These operations are also handled from left to right, whichever comes first. Addition does not always come before subtraction.
10−3+2
First, perform the subtraction
7 + 2 = 9
Let’s solve a complex example step-by-step:
Parentheses
3
3+54÷93+6=9
Thus, the final result is .
Understanding and applying
PEMDAS ensures that mathematical expressions are interpreted and solved
correctly.
-
Free Mock Test Schedule

Slots: 86JOIN MOCK TESTAM and PM
12:00, 4:00, and 8:00
We make our server run smoothly base on time schedule. -
Related Topics
-
Other Categories
- View Subscription
-
Join to our Facebook Page
09364813445
Solution
Qualification and Requirements
To be qualified to take the CSE-PPT, applicants must meet the following requirements:
| - | Filipino citizen |
|---|---|
| - | At least eighteen (18) years old on the date of filing of application; |
| - | Of good moral character; |
| - | Has not been convicted by final judgment of an offense or crime involving moral turpitude, disgraceful or immoral conduct, dishonesty, examination irregularity, drunkenness, or addiction to drugs; |
| - | Has not been dishonorably discharged from military service or dismissed for cause from any civilian position in the government; and |
| - | Has not taken the same level of Career Service Examination, either through PPT or CSC Computerized Examination, within three (3) months before the date of exam or from 03 December 2023 to 02 March 2024. |
The requirements to be submitted include: |
|
| - | Fully accomplished application form (CS Form No. 100, revised September 2016); |
| - | Four (4) pieces of identical passport-size ID pictures with name tags (read the examination advisory for the complete specifications); |
| - | Original and photocopy of any of the following accepted ID cards: Driver’s License/Temporary Driver’s License/Student Driver’s Permit; Passport; PRC License; SSS ID; GSIS ID (UMID); Voter’s ID/Voter’s Certification; BIR ID (ATM type/TIN card type with picture); PhilHealth ID (must have the bearer’s name, clear picture, signature and PhilHealth number); Company/Office ID; School ID; Police Clearance/Police Clearance Certificate; Postal ID; Barangay ID; NBI Clearance; Seaman’s Book; HDMF Transaction ID; PWD ID; Solo Parent ID; Senior Citizen’s ID; CSC Eligibility Card; Philippine Identification or PhilID Card; and |
| - | Examination fee of PHP500. |
Subscription
₱ 30.00
Basic
1 Account
Review Materials
Printable Mock Test
Advance Filter
Performance Monitoring
Basic
Step 1: Prepare your valid email address.
Step 2: Read the Terms and Condition. Click here!
Step 3: Make payment through G-Cash
Step 4: Submit your proof of payment (Gcash screenshots with reference number and email address) to the messenger chatbox found on the website.
Step 5:Wait for the administrator's response while creating your account.
Terms and Conditions
These Terms and Conditions govern your access to and use of the services provided by our system, including the 3 Months Mock Test, Downloadable Review Materials, Printable Mock Test, Advance Filtering, and Performance Monitoring. By accessing or using our Services, you agree to be bound by these Terms. If you do not agree to these Terms, please do not avail our Services.
1. Account Usage:We will create your account after you send your proof of payment through the chatbox found on the website to access our Services. Your account is personal to you and may not be shared with or transferred to another individual. You agree not to disclose your login credentials to any third party.
2. Simultaneous Device Usage:You may only be logged into your account on one device at a time. Logging into your account on multiple devices simultaneously is prohibited. If you attempt to log in on a second device while already logged in elsewhere, you may be automatically logged out from the previous session.
3. Acceptance of Policy:By using our Services, you acknowledge and agree to abide by these Terms and any other policies or guidelines referenced herein. You understand that your continued use of our Services constitutes acceptance of these Terms and any subsequent modifications thereto.
4. Privacy:Your privacy is important to us. We are not collecting any personnal information of yours.
5. Termination:We reserve the right to suspend or terminate your access to our Services at the time your account expires, with or without cause and without prior notice or liability.
6. Limitation of Liability:To the fullest extent permitted by law, we shall not be liable for any direct, indirect, incidental, special, consequential, or punitive damages arising out of or in connection with your use of our Services.
7. Changes to Terms:We reserve the right to modify or replace these Terms at any time. Any changes will be effective immediately upon posting the revised Terms on our website or notifying you via email.
8. Contact Us:If you have any questions or concerns about these Terms, feel free to contact us the chatbox found on the website.
By accessing or using our Services, you acknowledge that you have read, understood, and agree to be bound by these Terms and any other policies or guidelines referenced herein. If you do not agree to these Terms, please refrain from using our Services.
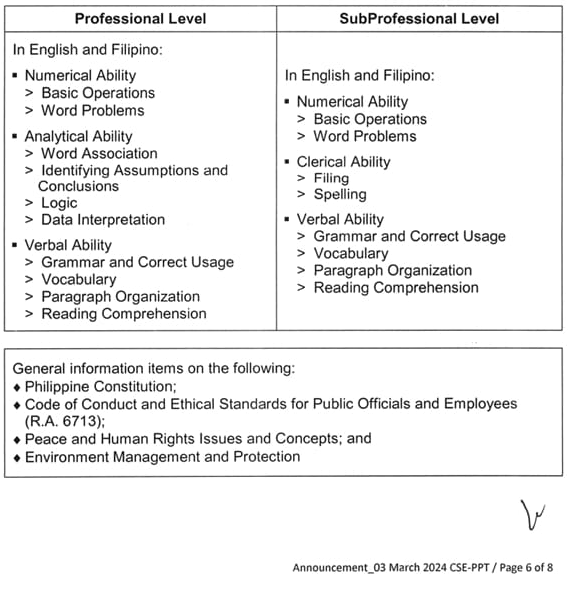
Scope of Examination
Choose Exam Level
Your Information
This is NOT an official EPS-KLT.
It's a customized computer-based test to help you prepare to pass the exam.
Purpose:
This website is intended to help all aspirants who want to experience the actual CBT-Exam or CBT (Computer Based Test).
We are Filipino just like you. Our intention is to help aspirants experience the actual CBT exam. We don't need your personal information in the website, NO REGISTRATION is required. We are just like you, helping one another to achieve our dreams.
Working together and supporting each other can greatly increase the chances of achieving our dreams. When we help others, we create a positive atmosphere that allows everyone to grow and succeed. Additionally, by sharing our resources, knowledge, and skills, we can overcome challenges and reach our goals more efficiently. Collaborating with others can also lead to new opportunities and ideas that we may not have considered on our own. By helping one another, we create a sense of community and increase our chances of achieving our collective dreams.
Guide How to Avail Free and Requested Passcode: Click Here!
Notice: We are still working on iOS.
Temporary Unavailable
This website is temporarily unavailable in requesting passcode based on your feedback we received, but still you can use some of the features of the website.
For those who already had a requested passcode you can still use it by log-in form provided.
Ishihara Test
Granting your request.
Your advice to use a Laptop or PC for best experience




